吃透Netty源码系列四十九之WebSocket编解码器详解二
Utf8FrameValidator
今天把剩下的一些说下,这个是验证文本帧是否是UTF8编码的。来看下吧。其实他就是检查是否是最后一帧,如果是文本帧的话就检测内容,不是UTF8的就抛异常。如果是持续帧,只有第一帧是文本的才会开始检测,所以后续来的肯定是文本帧,就不用判断是不是文本帧了,只要判断是不是在检测就好了。
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof WebSocketFrame) {
WebSocketFrame frame = (WebSocketFrame) msg;
try {
if (((WebSocketFrame) msg).isFinalFragment()) {//是最后帧
if (!(frame instanceof PingWebSocketFrame)) {
fragmentedFramesCount = 0;
// Check text for UTF8 correctness监测文本帧
if ((frame instanceof TextWebSocketFrame) ||
(utf8Validator != null && utf8Validator.isChecking())) {
// Check UTF-8 correctness for this payload
checkUTF8String(frame.content());
// This does a second check to make sure UTF-8
// correctness for entire text message
utf8Validator.finish();//如果不是就报异常
}
}
} else {//不是最后帧
// Not final frame so we can expect more frames in the
// fragmented sequence
if (fragmentedFramesCount == 0) {//是第一帧,只检测文本
// First text or binary frame for a fragmented set
if (frame instanceof TextWebSocketFrame) {
checkUTF8String(frame.content());//检测内容
}
} else {//不是第一帧,继续检测,因为前面是文本的,所以持续帧也肯定是
// Subsequent frames - only check if init frame is text
if (utf8Validator != null && utf8Validator.isChecking()) {
checkUTF8String(frame.content());
}
}
// Increment counter
fragmentedFramesCount++;//帧数累加
}
} catch (CorruptedWebSocketFrameException e) {
frame.release();
throw e;
}
}
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
WebSocketServerProtocolHandler
最后还得经过他呀。
decode
主要是判断是不是关闭帧,是的话就拿出开始创建的握手对象,然后实现关闭,其实就是发送关闭帧。否则的话就让父类WebSocketProtocolHandler处理。
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, WebSocketFrame frame, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (serverConfig.handleCloseFrames() && frame instanceof CloseWebSocketFrame) {//如果要处理关闭帧
WebSocketServerHandshaker handshaker = getHandshaker(ctx.channel());
if (handshaker != null) {
frame.retain();
handshaker.close(ctx.channel(), (CloseWebSocketFrame) frame);//握手处理器来处理关闭
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);//直接处理
}
return;
}
super.decode(ctx, frame, out);
}
WebSocketProtocolHandler的decode
如果是心跳ping,pong帧的就响应,然后继续监听读消息,否则就将数据帧加进消息列表中。
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, WebSocketFrame frame, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (frame instanceof PingWebSocketFrame) {//ping帧,写回pong,继续监听读事件,直接返回
frame.content().retain();
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(new PongWebSocketFrame(frame.content()));
readIfNeeded(ctx);
return;
}
if (frame instanceof PongWebSocketFrame && dropPongFrames) {//丢弃pong帧
readIfNeeded(ctx);
return;
}
out.add(frame.retain());
}
WebSocket08FrameEncoder解码器
其实编码器看懂了,解码器就是反的来,其实就根据情况吧数据封装成协议的格式。
比如封装成帧。
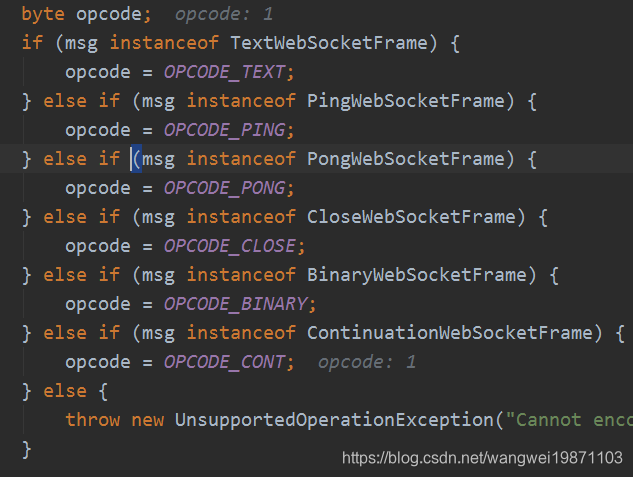
封装第一个字节:
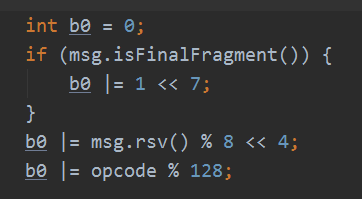
处理长度:
boolean release = true;
ByteBuf buf = null;
try {
int maskLength = maskPayload ? 4 : 0;
if (length <= 125) {//长度0-125
int size = 2 + maskLength;
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
size += length;
}
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);//前面2个字节+掩码长度(4字节)+内容长度
buf.writeByte(b0);
byte b = (byte) (maskPayload ? 0x80 | (byte) length : (byte) length);
buf.writeByte(b);
} else if (length <= 0xFFFF) {//内容2字节长度
int size = 4 + maskLength;
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
size += length;
}
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);
buf.writeByte(b0);
buf.writeByte(maskPayload ? 0xFE : 126);
buf.writeByte(length >>> 8 & 0xFF);
buf.writeByte(length & 0xFF);
} else {//内容8字节长度
int size = 10 + maskLength;
if (maskPayload || length <= GATHERING_WRITE_THRESHOLD) {
size += length;
}
buf = ctx.alloc().buffer(size);
buf.writeByte(b0);
buf.writeByte(maskPayload ? 0xFF : 127);
buf.writeLong(length);
}
处理掩码,这里默认服务器返回一般不用掩码,而且这里有一种优化,数据不过不太大的话,就合并成一个缓冲区一起发送:
// Write payload
if (maskPayload) {//掩码编码
int random = (int) (Math.random() * Integer.MAX_VALUE);
mask = ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(random).array();
buf.writeBytes(mask);
ByteOrder srcOrder = data.order();
ByteOrder dstOrder = buf.order();
int counter = 0;
int i = data.readerIndex();
int end = data.writerIndex();
if (srcOrder == dstOrder) {
int intMask = ((mask[0] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((mask[1] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((mask[2] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (mask[3] & 0xFF);
if (srcOrder == ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN) {
intMask = Integer.reverseBytes(intMask);
}
for (; i + 3 < end; i += 4) {
int intData = data.getInt(i);
buf.writeInt(intData ^ intMask);
}
}
for (; i < end; i++) {
byte byteData = data.getByte(i);
buf.writeByte(byteData ^ mask[counter++ % 4]);
}
out.add(buf);
} else {
if (buf.writableBytes() >= data.readableBytes()) {//可写长度如果大于等于内容大度,就合并成一个就发一次
buf.writeBytes(data);
out.add(buf);
} else {
out.add(buf);
out.add(data.retain());
}
}
release = false;
其他相关的自己可以看看,都比较好理解的,比如像配置类WebSocketDecoderConfig,关闭状态类WebSocketCloseStatus,关闭帧处理器WebSocketCloseFrameHandler。
最后再看下具体的例子:

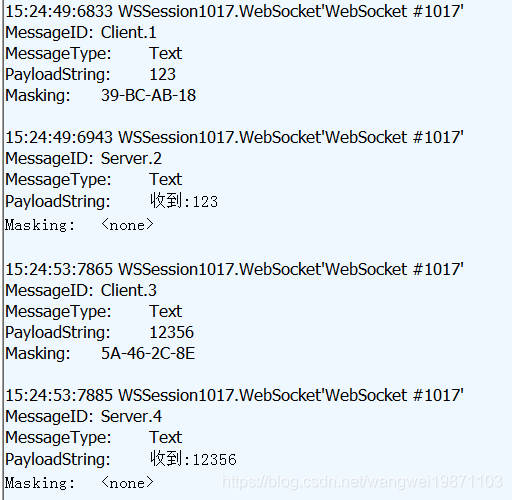
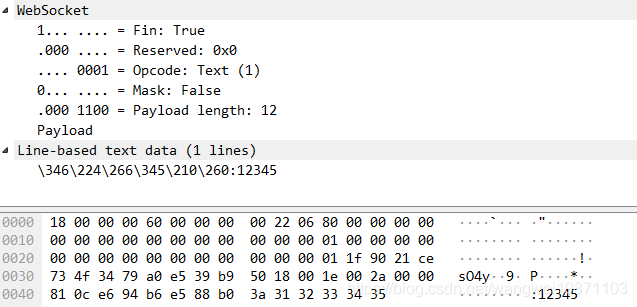
可以看到,客户端是有掩码的,服务端默认没有。
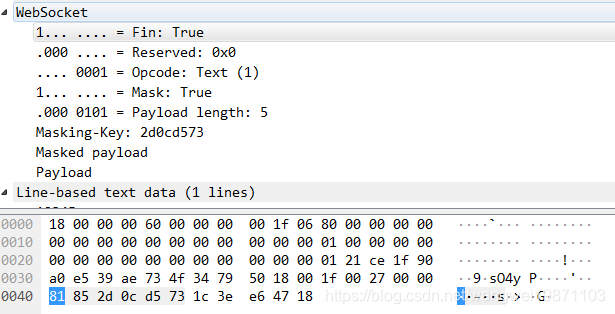
换个软件看,可能更详细点,客户端发12345,服务端发收到:12345:
好了,今天就到这里了,希望对学习理解有帮助,大神看见勿喷,仅为自己的学习理解,能力有限,请多包涵。

